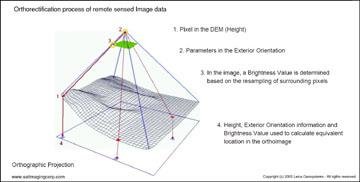
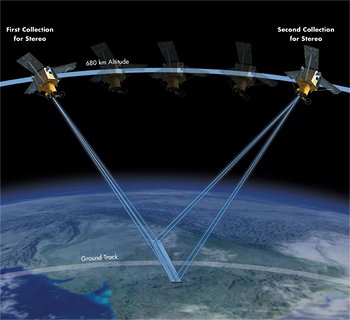
About Orthorectification
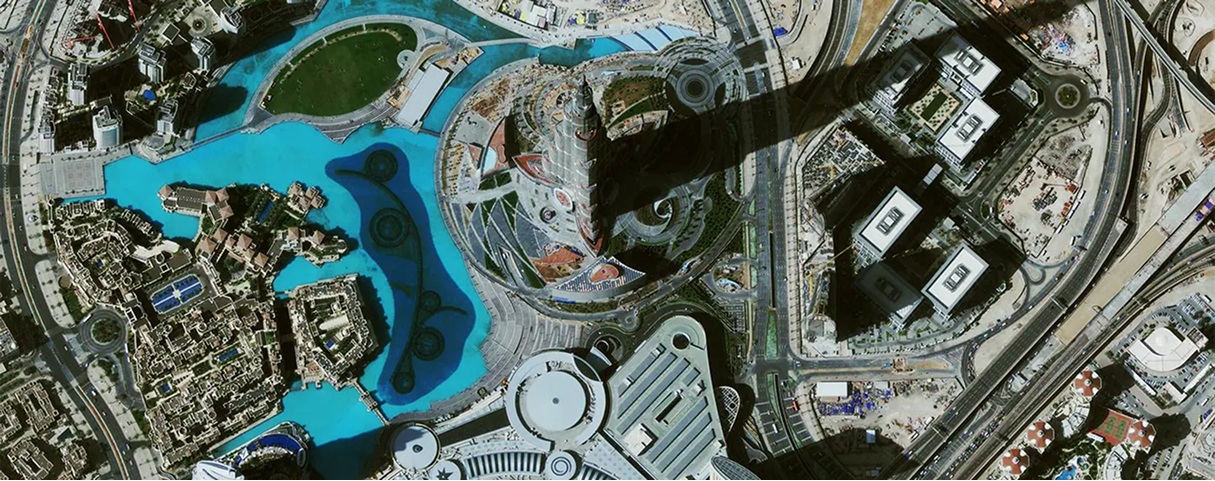
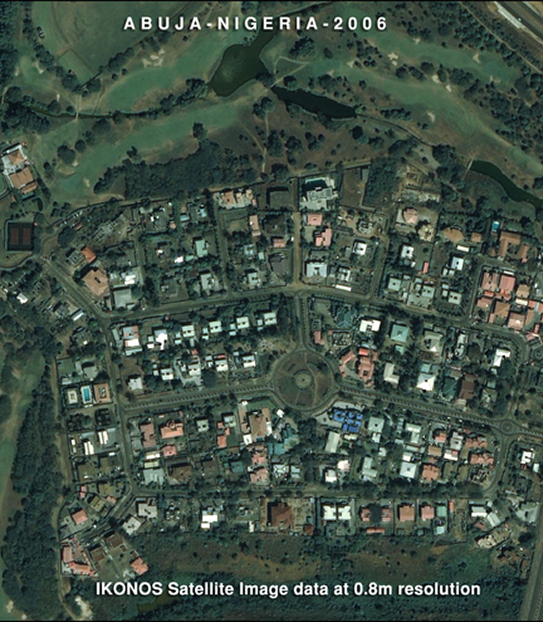
Remote sensing satellite and aerial imagery play an important role in Geospatial mapping by acquiring image data acquisition and visualization that can produce super GIS maps for many applications requiring precise and accurate data. Image data can provide a solid visual effect and is able to put spatial concepts into perspective when viewing or analyzing the data. In addition, image data can provide a basis for gathering spatial information to produce a GIS mapping environment. Features that can be extracted from imagery such as roads, vegetation, infrastructure, bridges, pipeline, and hydrology can be extracted. The image data must be processed to remove distortion to set the precise location of an area. This process is called orthorectification. Without this process, you would not be able to make direct and accurate measurements of distances, angles, positions, and areas.
What is Orthorectification?
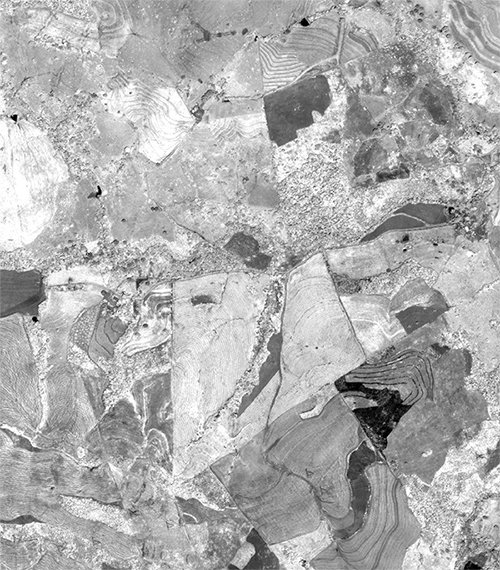
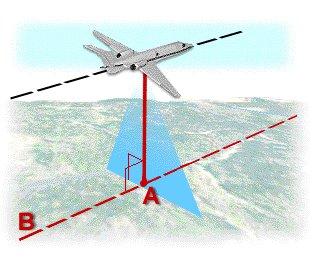
The topographical variations in the surface of the earth and the tilt of the satellite or aerial sensor can affect the distance with which features on the satellite or aerial image are displayed. The more topographically diverse the landscape, the more distortion inherent in the image.
Image data acquired by satellite or aircraft are affected by a systematic sensor and platform-induced geometry errors, which introduce terrain distortions when the sensor is not pointing directly at the Nadir location of the sensor.
Terrain displacement can be hundreds of meters. For example, if the IKONOS satellite sensor acquires satellite image data over an area with a kilometer of vertical relief, with the sensor having an elevation angle of 60° (30° from Nadir), the image produced will have nearly 600 meters of terrain displacement. Additional terrain displacement can result from errors in setting the reference elevation. Low elevation angles of images, imperfect terrain models, variability of sensor azimuth, and elevation angles within an image limit accuracy potential if image orthorectification is attempted. For this reason, when new high resolution image data is acquired over rough terrain, high-elevation angles of the sensor is required.
A=Nadir B=Nadir Line
Digital Elevation Model (DEM)
To accurately remove the image distortions, a digital elevation model (DEM) is used to perform image orthorectification. The required DEM is generated by feature extraction from high-resolution stereo satellite imagery.
For many international products where DEMs are not available with a posting interval of 90m, Satellite Imaging Corporation (SIC) utilizes the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) 90m DEM data set for the orthorectification of satellite image data. When higher mapping accuracy standards are required the DEM is extracted from existing topographic maps at an acceptable scale or acquired by stereo satellite image data providing a DEM posting and accuracies is standard with high-resolution stereo satellite sensors. At this accuracy, standard GPS derived ground control points (GCPs) are required. Other remote sensing techniques are also utilized, such as radar interferometry or LiDAR.
SIC performs the orthorectification of images of environmental, geological, topographic, or any source maps that are used in a GIS mapping environment.
Consultancy
Ongoing Satellite remote sensing and GIS consultancy services are provided to our clients, including the set-up of reliable source coordinate databases in support of computerized mapping, exploration, and development of projects around the world and to clients implementing AI, ML, Computer Vision (CV), or GIS management systems utilizing a variety of source data. For more information or for a consultation, please contact us.
For more information on any of our products and services or for a consultation, please contact us.