GIS Mapping Services
“SIC’s Expertise Prevents Potential Problems….”
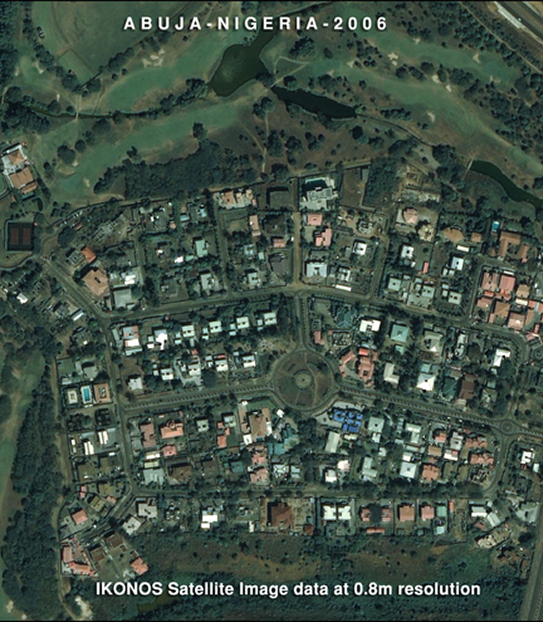
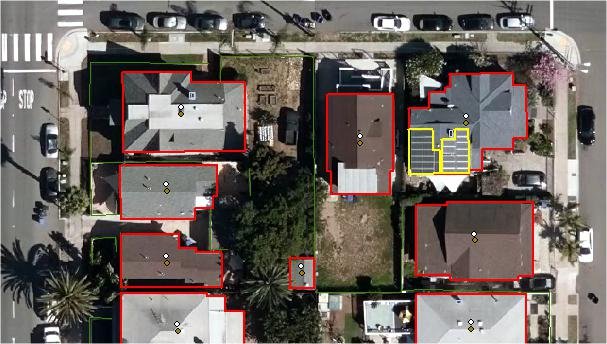
Satellite Imaging Corporation (SIC) combines orthorectified satellite imagery with extracted vector data and client-supplied geospatial data to create single, GIS data-rich maps for various industry applications including agriculture, disaster management, energy, and environmental monitoring. SIC incorporates GIS data to achieve a multi-layered result for many types of analysis and management pertaining to your project. The expertise and accuracy of our GIS mapping services preclude nearly all potential problems associated with GIS maps.
By utilizing GIS, Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML) neural network algorithms, and satellite remote sensing techniques, automated extraction of objects detected on satellite imagery can expedite and reduce the cost of e.g. monitoring wildlife, detection of solar panel arrays on commercial and residential buildings, detection of objects similar in shape or materials or other suitable applications, such as precision agriculture mapping etc.
Our GIS mapping services allow us to capture, store, manipulate and analyze geospatial data to combine database, mapping. and statistical methods to integrate georeferenced data for data collection, processing, and management ensuring accurate solutions that allow you to overcome tough challenges pertaining to your project. Our focus is to deliver accurate quality geospatial products to help manage your mapping goals.
Some projects are hampered by coordinate problems of different satellite image and vector data layers, which are caused by one or a combination of the following:
Improper orthorectification of satellite imagery or aerial photography
Use of different survey datums and/or geodetic parameters
Poor quality of GPS derived ground control points (GCPs)
Improper rectification of digital source raster maps
Importation of vector data or shape-files for source data with incorrect coordinates
Improper use of units or unit convergence factors for source data
Utilization of source data from a corrupt coordinate database
Our team is committed to quality control and provides continuing geodesy, mapping, ArcGIS 2D, and 3D geospatial support services to our clients. We ensure that the geospatial data sets provided to our clients is utilized in only the most effective manner. On every GIS project, whether large or small, we implement ongoing data quality control to ensure that coordinate databases, foreign source data such as geological, topographic maps, GIS data attributes, and layers create a truly seamless GIS mapping environment.
Our in-house knowledge in geodesy, land and hydrographic surveying, 2D/3D digital mapping, GIS, and satellite remote sensing applications will provide the most professional service and products to our clients.
One of the primary service provided by SIC during the implementation of a GIS project is the georeferencing of various GIS data layers for mapping projection. SIC has developed comprehensive policy and procedures to include QA and QC in the planning stage of every project involving the use of satellite image data for geographical information systems mapping including:
Topographic Mapping
Consultancy
Ongoing Satellite remote sensing and GIS consultancy services are provided to our clients, including the set-up of reliable source coordinate databases in support of computerized mapping, exploration, and development of projects around the world and to clients implementing AI, CV, or GIS management systems, utilizing a variety of source data. For more information or for a consultation, please contact us.
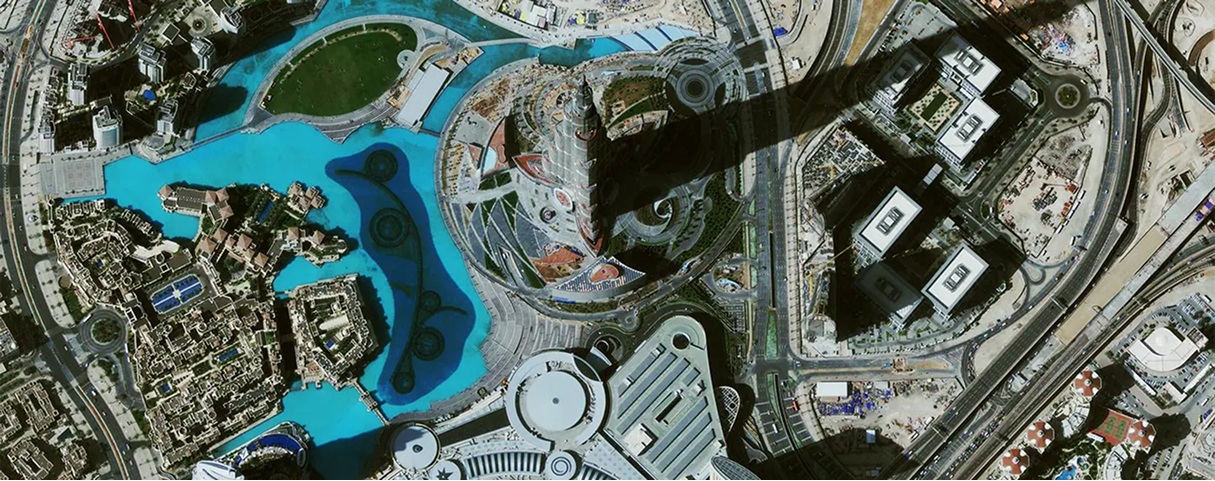

Rapid Acquisition / Rush Tasking
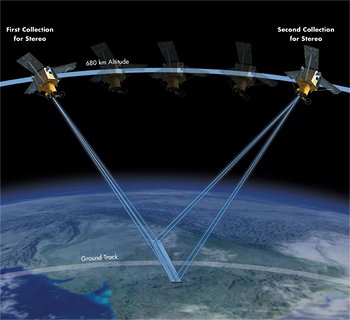
RUSH tasking orders for satellite image data around the world are accepted by SIC in support of live events, natural disasters, global security, and various other applications in which FAST delivery of image data is critical. In most instances, we can provide image data within 24 hours after the initial data has been acquired and delivered via FTP.